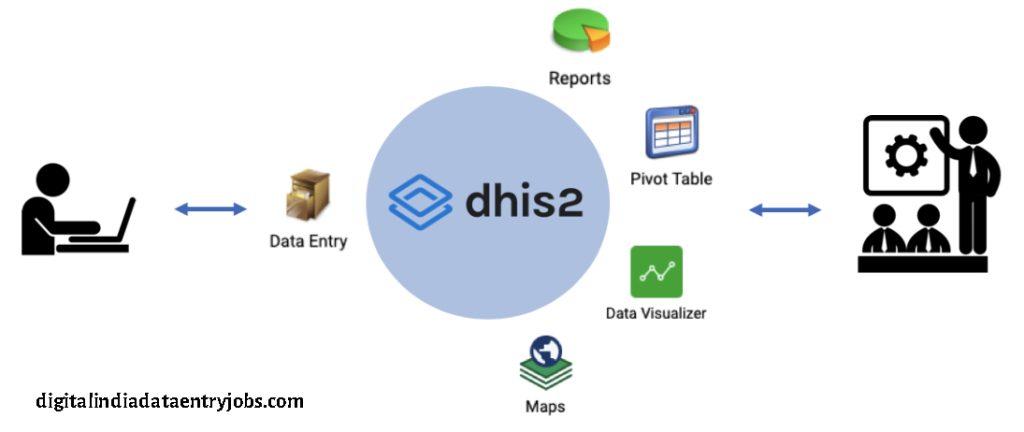
DHIS2 Data Entry:- DHIS2 is a web-based health management information system (HMIS) that is available for free. The University of Oslo’s HISP group is responsible for the development and management of this DHIS2 core software.
With more than 72 nations using DHIS2, it is currently the largest HMIS system in existence.
A common, elementary example would be the reporting of the total number of vaccinations administered at health facilities across the nation; this could include the number of individuals immunized against particular diseases, or the number of people who died or became infected for various reasons within particular districts and regions. Following data collection and submission in DHIS2, a range of analytical tools are available for data analysis and presentation, including pivot tables, charts, and maps. Decision-makers develop interventions to improve healthcare services using this information.
Contents
DHIS2 Data Entry
Over 40 countries worldwide use the District Health Information Software (DHIS). With a focus on integrated health information management, DHIS 2 is a tool for gathering, verifying, analyzing, and presenting statistical data based on patients and aggregates. It’s a tool that lets the user create the contents of a particular information system without requiring programming knowledge thanks to its open meta-data model and adaptable user interface. Using free and open-source Java frameworks, DHIS2 and later versions are modular web-based software packages.

Also Read:- Government Online Data Entry Jobs Without Investment
A lack of fundamental health and demographic record-keeping is the reason for the under-documentation of health data and information. With this training, the SID Institute hopes to increase the ability of researchers, health record managers, and practitioners to monitor, manage, and preserve health information and demographic data in a far more accurate and efficient manner than paper records. With the completion of this DHIS 2 installation, use, and maintenance training course, participants will have the skills and knowledge needed to report, analyze, and distribute data for all health initiatives.
PERSONS WHO Ought to Attend?
- Researchers, field workers, health administrators, and officers in charge of health information systems
OBJECTIVES
- DHIS 2 configuration
- Recognize the functions of DHIS 2 in health information systems (HIS). The main features of DHIS 2 support data collection, validation, visualization, presentation, and information use.
- Which technological factors are the most important to take into account when implementing DHIS 2?
- Data entry and gathering; Data analysis and visualization; DHIS 2 data quality;
- Data components, sets, and indicators; event recording, event reporting, event visualizer, and tracker recording
- Setting up DHIS 2 to track progress against goals such the international development goals and health-related metrics
- What are the advantages and difficulties associated with DHIS use?
RELATED TOPICS
Module 1: Overview of DHIS 2 and Utilisation of Information
- Concepts related to health information management
- Decision-makers and planners in the health sector require several types of data.
- Data sources
- Requirements for law and ethics
- DHIS2 Organisational units’ advantages
- Cycle of information
Task: Enumerate the information systems utilized by the healthcare system.
Module 2: DHIS2 Software’s Basic Operation and Usage
- Installation of DHIS 2
- Key terms
- Components of DHIS2
- Strategy for getting started
- Indicators
- Data element
- Data sets and data entry forms
- Data set management
- Data set categories
- Adding a new section form
- Customs forms
- Scripting in custom forms
- Data assignment editor
- Pivot table design
- Connecting to the DHIS2 database
- Dealing with large amounts of data
- My datamart tool
Also Read:- Part-Time Data Entry Jobs Part-Time
Practice: Creating pivot tables
- Data visualization
- Charts and graphs
- Charts and dashboards
Task: Creating diagrams
MODULE 3: DATA DESIGN AND COLLECTION
- Data set
- Data set management
- Data set categories
- Data entry forms
- Adding a new section form
- Customs forms
- Scripting in custom forms
- Data assignment editor
Practice entering data

MODULE 4: GIS MAPS
- Introduction to GIS
- The usefulness of GIS maps
- Thematic layer
- Maps consideration
- Editing and navigation
Practice: making DHIS2 maps
Module 5: Validation and Quality of Data
- Measuring data quality
- Reasons for poor data quality
- What makes quality data
- Common data quality check
- Data validation analysis
- Validation rules
- Improving data quality
Exercise: Encouraging better data quality with DHIS 2
MODULE 6: APPLICATION STRATEGY
- Processing data analysis
- Updating data and controlling database modifications
- Setting up meta-data
- Data import and export Aggregation
- Putting together reports and other informational materials
Key Features of the DHIS2
- Local adaption and customization via the user interface. Utilizing DHIS2 in a new environment (country, region, district, etc.) doesn’t require programming.
- Flexible and dynamic (on-the-fly) data analysis is available in the analytics modules (e.g., Geographic Information Systems-GIS, PivotTables, Data Visualizer, Event reporting, etc.).
- A dashboard tailored to each user that provides rapid access to all pertinent monitoring and assessment tools, such as indicator charts and shortcuts to favorite reports, maps, and other important system resources.
- Simple to use user interfaces for managing metadata, such as those for adding or changing datasets or medical facilities. To configure the system in a new environment, no programming is required.
- the ability to create and alter computed indicator formulas.
- features for data and metadata export-import, facilitating offline installation synchronization and facilitating application interoperability.
- The capacity to extend the main platform through the usage of custom apps and interfaces with additional technologies.
Also Read:- How to Work in Data Entry With Example
DHIS2 Data Entry: Uses of DHIS2
The following uses for DHIS2 are possible:

- Gathering information.
- Carrying out quality assurance.
- Numerous tiers of data access.
- Reporting.
- Creating maps, graphs, and other analytical tools.
- Facilitating comparisons over distance (e.g., between facilities and districts) and time (e.g., prior months).
- Putting data into a time series so you can observe its lowest and greatest levels
Example use
The reporting of the number of vaccinations administered in a medical facility is a common, elementary example. Decision-makers must be aware of the vaccination rates for particular diseases in various districts. This instance involves creating a data entry form in DHIS2 with multiple data components that indicate the variety of immunizations administered. For example, the medical staff at a clinic will routinely (e.g., once a month) complete this form on the computer and submit the values. An indicator in DHIS2 that indicates the vaccination status in that district—that is, the proportion of the population that has received vaccinations—can be constructed by combining the number of vaccinations administered that are provided on the form with demographic information. National health managers can view data by region, state, etc. by aggregating the data.
Suggested Link:- indnewsupdates.com
#Saras